Rerank-for-better-RAG-(Explained)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K1F8BIgcoNk
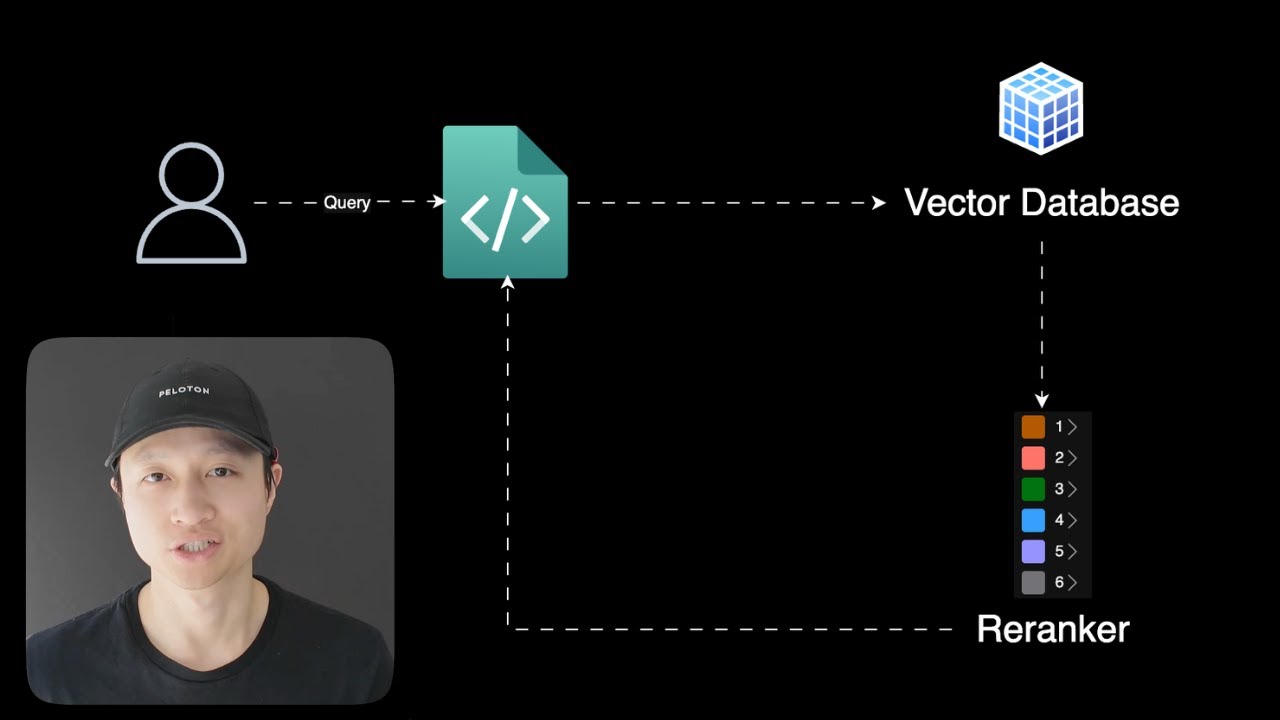
Today I want to talk to you about re-ranking. So you should always treat your retrieval augmented generation problems as a search problem. What that means is you can use tools from search, and one of the best tools you can use is re-ranking. RAC system, or retrieval augmented generation system, looks something like this. You have the user sending a query to an application, and then the application send that query in the form of vectors to a vector database, like Pinecone, VV8, or PGVector. But large language models don't have infinite context. And we have this thing where we want to increase recall, which means if there are 20 or 30 or 40 accurate documents in my vector database, I want to be able to retrieve as many of those as possible, which means a lot of times in real-world scenarios, you're going to have to be over-retrieving to get more than you need in order to get that recall number up. So in that case, we rely on the large language model to make sense of both the relevant information and the irrelevant information. So how can we help the LM make a more accurate final generation of the answer? So that's where WeRanker comes in. And let me just show you a quick explanation of what that means. Here, I have a search query about Sabrina Carpenter's song. And I want to look for a very specific song, which is about coffee. But here, what happened is we over-retrieved, so we got four songs here. But just from looking at this, you know that the song at the bottom, Espresso, is the one that we want, right? Because it's about coffee. However, it's at the bottom. And if we were to send this to our super, super, super small LM, it will look at all fours of these songs and kind of like maybe hallucinate a little bit because it doesn't know which one is actually the one that we want. So with the Reranker in play, what's going to happen is it puts the most relevant content at the top while kind of like reducing the rank or the position of the content that are not as relevant. The way that Rerankers work, especially for the more modern ones like the one from Cohere or from Gina AI, is that it actually uses LLM to understand the context of the documents and the trunks that it comes back and then rank them accordingly. If you want to look more into what these re-rankers do, so Cohere is a great provider for a service for re-ranking that you can use for your application. So right now, what I'm going to do is I'm going to show you an example of using Cohere Reranking with my existing Rack application. And we're just going to treat the Rack part as a black box right now. And after I show you this, I'm going to show you a better way to do it where I don't even have the set of coherent re-ranking or any re-ranking service at all in my application because I'm going to be using a service that provides both retrieval and re-ranking in one place. So what's going to happen is I send a question that says, what is Jeff Bezos' leadership philosophy? So my knowledge base is basically I web scraped or crawled through this website called Founders Tribune and it has a bunch of like articles about like you know startups and founders and stuff like that anyone from like Steve Jobs to like Jeff Bezos. And I'm asking specifically about Jeff Bezos. So my retrieval system retrieved 10 documents. And then after that, it takes those documents and it re-ranks them. And then after re-ranking is done, it's going to take the top five with the highest relevancy scores because these re-ranking services gives you a score. And then it's going to pass those documents. Actually, it's going to concatenate all those documents' content into one big string and then pass that into our an LLM in this case it's a llama 3.18 billion took parameters instruct turbo from together AI and then finally we get a kind of final generation from the LLM which is you know takes into account the documents that were sent back and stuff like that so very simple and you can you do this in your application really easily so let me show you what it looks like in the code. So here when you go to this code base, you want to check out the manual way to do this, just go to manualreranking.py and then in here, let me just scroll to the bottom here, this is where the domain execution flow is. So here is my user query and then here is my function that runs the retrieval part and the re-ranking part. And then after we get that response from our re-ranking, we're going to pass that to our model. So that's right here, query model. And then finally, we get this nice object that says question result that has not only the original question, but also the re-ranked documents and then the response from the model. And then we're just going to print that out into the terminal. nice kind of emoji flooded terminal display here I love these things but the most important part here is let's take a look at how the relationship between like retrieving documents or retrieving chunks and re-ranking looks like in code so to do that you go to same file you go to like the process question function And then, as you can see, there are about one, two, three, four, five steps to get through it. From retrieving documents to having the documents ready to then pipe to a large language model. So first step, obviously, is to retrieve documents. This is just taking the query and then sending it to the vector database. We're not going to go into that today. step two is because cohere re-ranking kind of requires you to have a certain type of format that goes in and then when it comes out the other side it also has a certain type of format so a little bit of complexity for you there so you have to like transform your information a little bit while you're using this service or this tool so we retrieve the documents and then we going to extract two separate lists So the first list is the documents text so the content of the documents or the contents of the chunks when we say documents and chunks it literally the same thing whatever that comes out of the retrieval or the vector database and we also have document IDs and we're going to rely on the document ID to be able to after re-ranking know okay so which one is actually on top which one is because after re-ranking like things are shuffled so we have to rely on the ID of the chunk of the document to know, okay, the chunk that was at the bottom before is not at the top. So we can rely on that. And then finally we can pass it into our Reranker using this .rerank function, which comes with Cohere. And we pass in the user's question. That's one cool thing about Reranker, which is it actually takes into account the question and then see which document, which chunk is most relevant to the question. And then we pass in the document's text and the document's IDs. And keep in mind, because I've created these lists, like the order of the text content of the chunks and the order of the ID match. That's why I know that, okay, I don't have to worry about, okay, it's like which ID belongs to which document. And then we're going to specify top five here, so we only get the top five most relevant chunks or documents. even though in our retrieval system we're taking back 10 because we're over retrieving to get that recall up so that our re-ranking system have more has more documents or chunks to work with and i can increase that number to like you know 50 or something and then finally we can like i said concatenate all the content of the documents into one big string and then we're going to build a Let me show you the prompt real quick before we send it to our LLM. So it just says, based on the following information from Jeff Bezos, please answer this question. So we pass it into the original question in the prompt, which is just a string. And then we just stuff the context, which is all the content from the documents that are sent back from our Reranker. So it's five instead of ten. And the most relevant document will be at the top. So it'll be like, first one will be like the most relevant one. Cool, so a little bit of code, a little bit of complexity, and let me show you what it looks like to create the Reranker. So Coheres documentation is pretty straightforward. You just sign up for an account, and then you go and you get an API key. You set up, I have a Rerank method. So in here, you want to set your Reranking model to something like this. So there are many different models. And once in a while, there's a new one that comes out. And this is the reason why when you're building an application with so many providers, so many different moving pieces to it, you kind of forget that, oh, there's a better model out there that I should try. So it might make more sense in your case to use a service that kind of just bake in the best practices and the latest and greatest for you that have been battle-tested with other users and you know there's a lot of transformation here because like I said the documents coming in and documents coming out it the shape looks a bit different from like the original documents that are retrieved from your your Vector Database So lots of transformation code And feel free to take this code and build your own But I'm going to show you arguably a better way to do it, which means... And I don't like to think about the complexity of these things too much because they don't make or break the application on the product that I'm building. Reranking is just part of it, and less complexity feels better for me. So here I'm going to show you how to do it with my retrieval system, which I've been using this whole time, which is a rack pipeline on the service called Vectorize. Very similar setup, so you still have the user send in a query. The query hits your application, and the application talks to a service called Vectorize. And this service kind of hides away all the vector database complexities and re-ranking complexities, and you just communicate directly with just the service. So let me show you how it looks. So here we have another script called built-in re-ranking. And it looks very similar to what we had before. We have one step, two step, three steps instead of five. So that's already way less complexity. And to retrieve the documents, because this function wraps around the service called vectorize, we can set a parameter called re-rank to true, which means that I don't have to transform anything. anything I don't have to pass these documents to another service when I retrieve documents I know that they are re-ranked for me and then still the same same deal you know everything like that so let's take a look at what's inside of this function here so against the still the same function that I use for my manual re-ranking but instead of re-ranking being false here I set it to true so that I can skip the step that I have to set up my coherent re-ranker so VictorRise is free to try and this is what my retrieval system looks like what I did was I set up a crawl job to go to the website here this page right here and and just scrape every single article from this website. And when you go to Vectorize, you have this really nice dashboard, and I was able to set this up on the GUI here, and then connect to it with my Python script using the retrieval endpoint. So that's the cool thing about Vectorize, which is you have your retrieval system, you have your vector database set up, you can crawl a website, or any data source you have. And then you have this one URL that you can hit. And then more importantly, this is all you have to do to have re-ranking set up with vectorize. So you skip all the complexities of setting up and managing a separate service like Cohere. And your application, all it knows is I have a retrieval system and I know that content from that retrieval system has been retrieved well and ranked properly. So I have both recall and precision. So that's it for the video today. So go out and try re-ranking your retrieval system and I'm sure it's going to increase your precision for whatever that you're retrieving. And your large sandwich model is going to love you for that. So thanks for watching.